- Center on Health Equity & Access
- Clinical
- Health Care Cost
- Health Care Delivery
- Insurance
- Policy
- Technology
- Value-Based Care
Tildrakizumab Shows Sustained Effectiveness, QOL Improvements for Psoriasis
Tildrakizumab showed early and sustained effectiveness and quality of life (QOL) improvements in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis across 2 studies.
Two posters presented at the 2025 American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Annual Meeting highlighted the efficacy and quality of life (QOL) improvements of tildrakizumab for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
Tildrakizumab showed early and sustained effectiveness and quality of life (QOL) improvements in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. | Image credit: Ban - stock.adobe.com
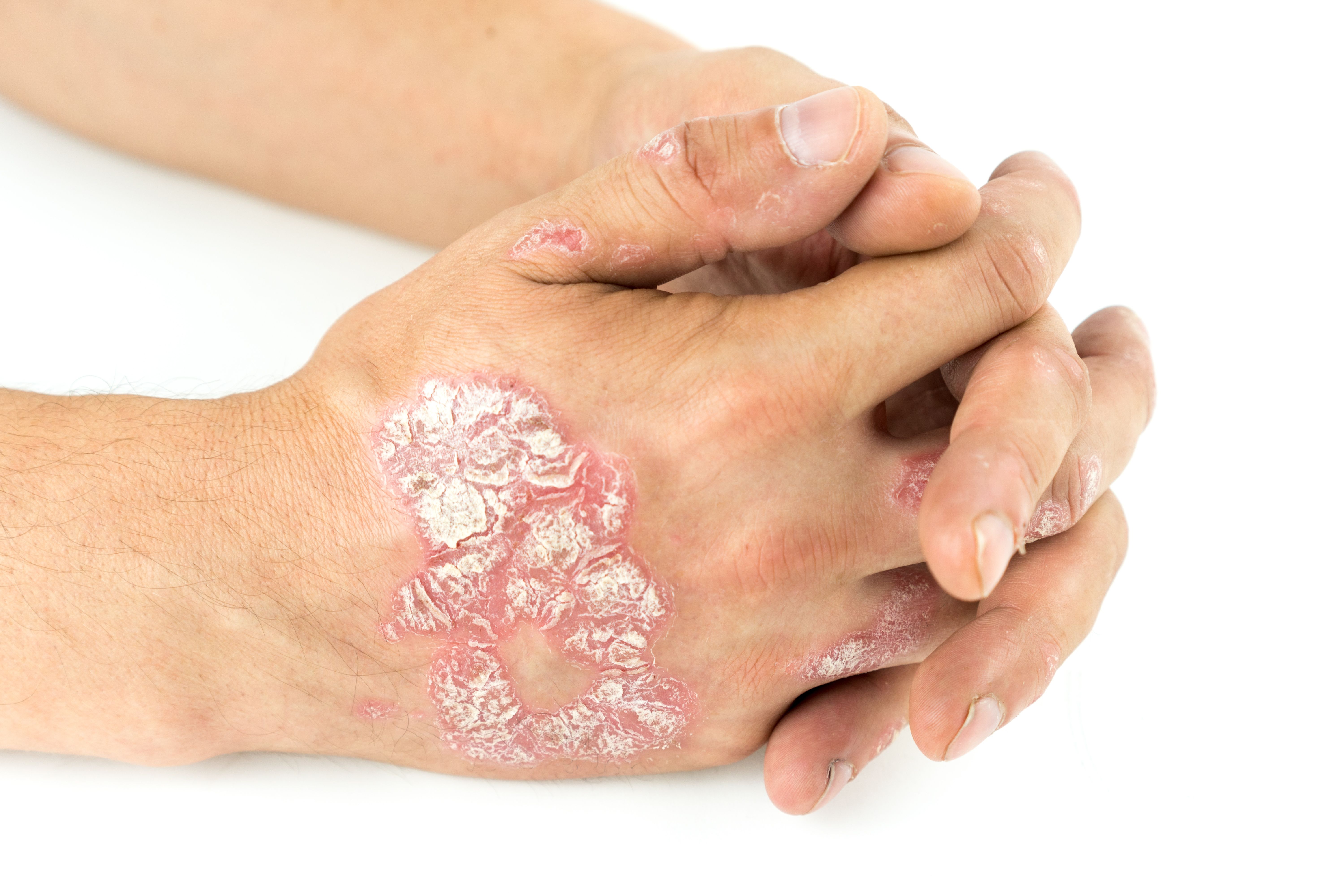
Tildrakizumab is an anti–interleukin-23 p19 monoclonal antibody used to treat patients with chronic moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.1
The first poster was based on a systematic literature review and meta-analysis that evaluated the real-world effectiveness of tildrakizumab and QOL in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in the US compared with the global population. The researchers based their study on MEDLINE, Embase, conference abstracts (2021-2023), and literature review bibliographies to identify real-world studies on tildrakizumab in patients aged 18 years and older. All studies were published in English.
The review included 3 US studies involving 110 patients—2 prospective and 1 retrospective—that demonstrated significant improvements in psoriasis severity over time. Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) decreased from 13.26 (95% CI, 9.23-17.28) at baseline to 1.57 (95% CI, 1.00-2.14) at 36 to 52 weeks, while the percentage of body surface area affected (BSA) dropped from 16.59% (95% CI, 12.1-21.08) to 2.77% (95% CI, 1.73-3.82) at 24 to 28 weeks.
Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) scores also declined from 3.34 (95% CI, 3.05-3.64) to 1.48 (95% CI, 0.89-2.06), and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores improved from 12.81 (95% CI, 5.86-19.77) to 3.16 (95% CI, 0.04-6.29) within the same timeframe. When compared with global findings across 37 studies, US results were consistent for PASI and BSA but showed higher PGA and DLQI scores, suggesting potential variations in patient response or treatment effectiveness across different populations.
These findings highlight tildrakizumab as an effective treatment with QOL improvements for patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.
The second poster was based on a retrospective, longitudinal, claims-based cohort study that aimed to describe clinical and demographic characteristics of patients with psoriasis treated with biologics tildrakizumab, risankizumab, guselkumab, or ustekinumab.2 Additionally, the study aimed to describe real-world treatment patterns, including time to treatment discontinuation (TTD), persistence rates, and treatment adherence. Patients were identified using claims data from April 1, 2018, to June 30, 2023.
TTD patterns defined discontinuation as a gap in consecutive claims of at least 3-times the days’ supply or between the last claim and the end of follow-up. Days’ supply was determined from claim data when available or imputed based on dosing schedules when missing. The study cohort included 338 patients on tildrakizumab, 14,621 on risankizumab, 10,824 on guselkumab, and 5,738 on ustekinumab, with a mean (SD) age ranging from 46.6 (12.7) to 48.5 (14.2) years and 46.7% to 52.1% female representation. Over a mean follow-up ranging from 16.8 (11.5) to 25.9 (17.3) months, median time to TTD varied significantly, with tildrakizumab demonstrating the longest persistence at 21.7 months, followed by guselkumab (17.7 months), risankizumab (12.6 months), and ustekinumab (11.2 months). At 12 months, persistence rates were highest for tildrakizumab (65.7%) and lowest for ustekinumab (48.3%). Discontinuation before the end of follow-up occurred in 38.5% to 57.8% of patients, while the proportion achieving a proportion of days covered of 80% or greater was highest for tildrakizumab (69.8%).
These results underscore the variability in biologic treatment patterns, with tildrakizumab demonstrating the longest persistence and highest adherence among the therapies studied.
References
1. Gottlieb S, Farberg AS, Bhatia N, et al. Real-world effectiveness and quality of life outcomes of tildrakizumab for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in the United States: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Poster presented at: 2025 AAD Annual Meeting; Orlando, FL; March 7-11, 2025.
2. Han G, Zanardo E, Simpson R, et al. Treatment patterns in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis treated with biologics. . Poster presented at: 2025 AAD Annual Meeting; Orlando, FL; March 7-11, 2025.
The Breakdown: Breast Cancer Research Awareness Day
August 19th 2025Breast cancer is the second most common cancer among women and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women in the US. In light of Breast Cancer Research Awareness Day, The American Journal of Managed Care® breaks down the most recent advancements in breast cancer prevention, screening, and therapies.
Listen
Psoriasis as an Inflammatory Disease, and What’s Changed Over Time
August 3rd 2021August is National Psoriasis Awareness Month, and on this episode of Managed Care Cast, we bring you an excerpt of an interview with a New Jersey dermatologist about the changing concept of psoriasis as more than just a skin disease.
Listen
