- Center on Health Equity & Access
- Clinical
- Health Care Cost
- Health Care Delivery
- Insurance
- Policy
- Technology
- Value-Based Care
Infographic: Differences in Personal Health Record Adoption by Sociodemographics
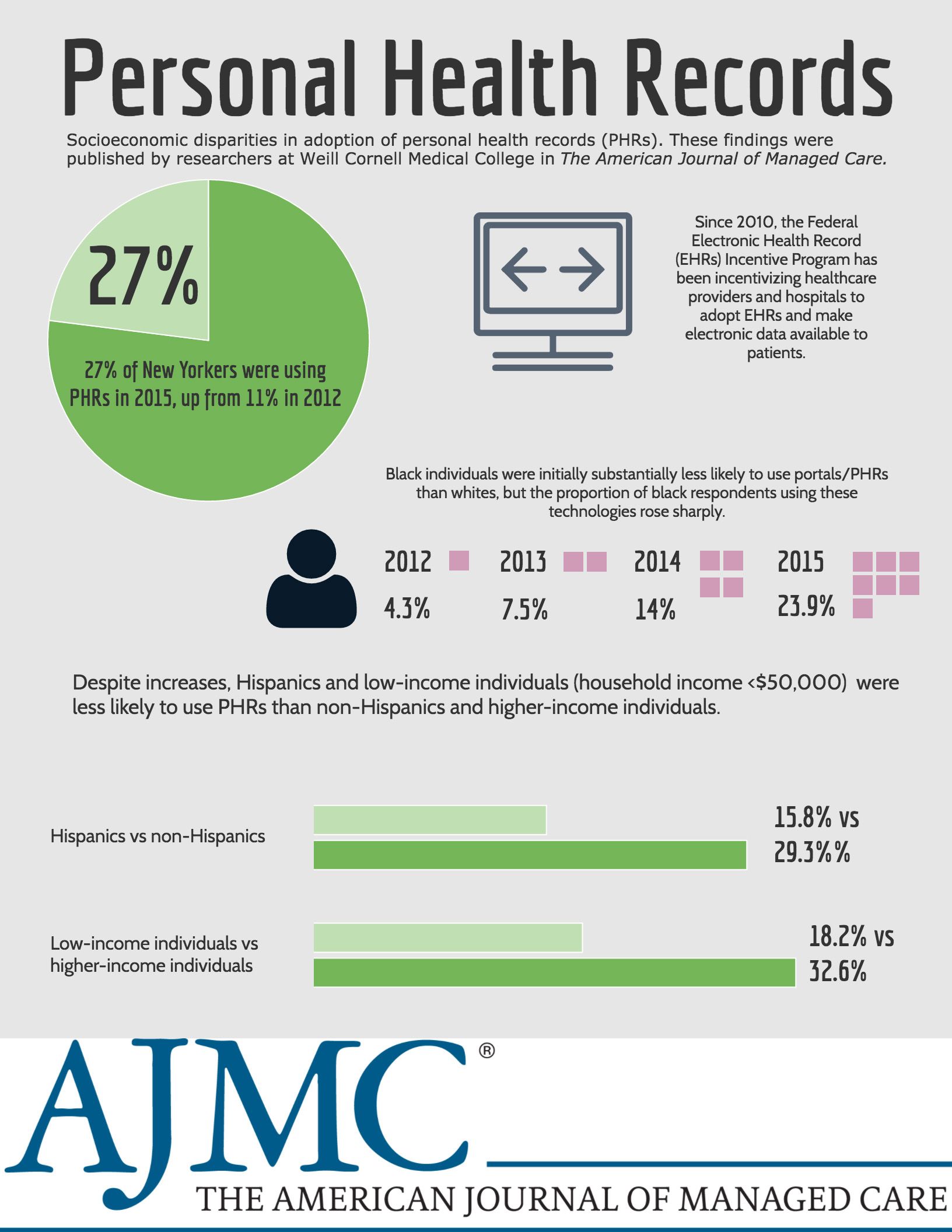
While adoption of personal health records and electronic patient portals increased from 2012 to 2015, researchers at Weill Cornell Medical found that the adoption rates for Hispanics and low-income individuals have lagged behind non-Hispanics and higher-income individuals.
While adoption of personal health records and electronic patient portals increased from 2012 to 2015, researchers at Weill Cornell Medical found that the adoption rates for Hispanics and low-income individuals have lagged behind non-Hispanics and higher-income individuals.
The Federal Electronic Health Record Incentive Program has been incentivizing healthcare providers and hospitals to adoption electronic health records and make electronic data available to patients. A randomized telephone survey of New Yorkers found that the proportion of New Yorkers using personal health records rose from 11% in 2012 to 27% in 2015. While black individuals were less likely to use personal health records and patient portals in 2012 compared with whites, the proportion of black individuals using these technologies rose sharply over the course of the survey.
However, the increased rate of Hispanics and low-income respondents (household income less than $50,000) using these technologies did not keep up.