- Center on Health Equity & Access
- Clinical
- Health Care Cost
- Health Care Delivery
- Insurance
- Policy
- Technology
- Value-Based Care
Gaps in Rheumatoid Arthritis Care Quality Exist in North America
A literature review plus in-person visits helped identify barriers to quality rheumatoid arthritis care, as well as effective interventions to improve care quality.
A literature review coupled with in-person visits to 9 rheumatology centers across the United States and Canada identified several challenges to delivering quality care for rheumatoid arthritis, as well as good practice interventions that can have a positive impact on care quality. The findings were published in ACR Open Rheumatology, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology.1
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition that causes joint pain and inflammation, and when left untreated, it can cause severe joint and tissue damage, as well as comorbidities related to the heart, lung, or nervous system.2 While not curable, the progression of rheumatoid arthritis can be managed with multidisciplinary care.
“Guidelines recommend a targeted approach for the management of RA and associated comorbidities,” the study authors wrote.1 “However, factors such as a decline in the rheumatology workforce continue to pose challenges, leading to poor patient satisfaction.”
The study aimed to provide insight on current challenges in the management of rheumatoid arthritis and its associated comorbidities, foster improvements in quality of care by identifying and documenting effective interventions by rheumatology teams and sharing possible strategies other rheumatology centers can use improve care.
The review identified several challenges to quality rheumatoid arthritis treatment, along with potential interventions to improve care. | Image Credit: MicroOne - stock.adobe.com
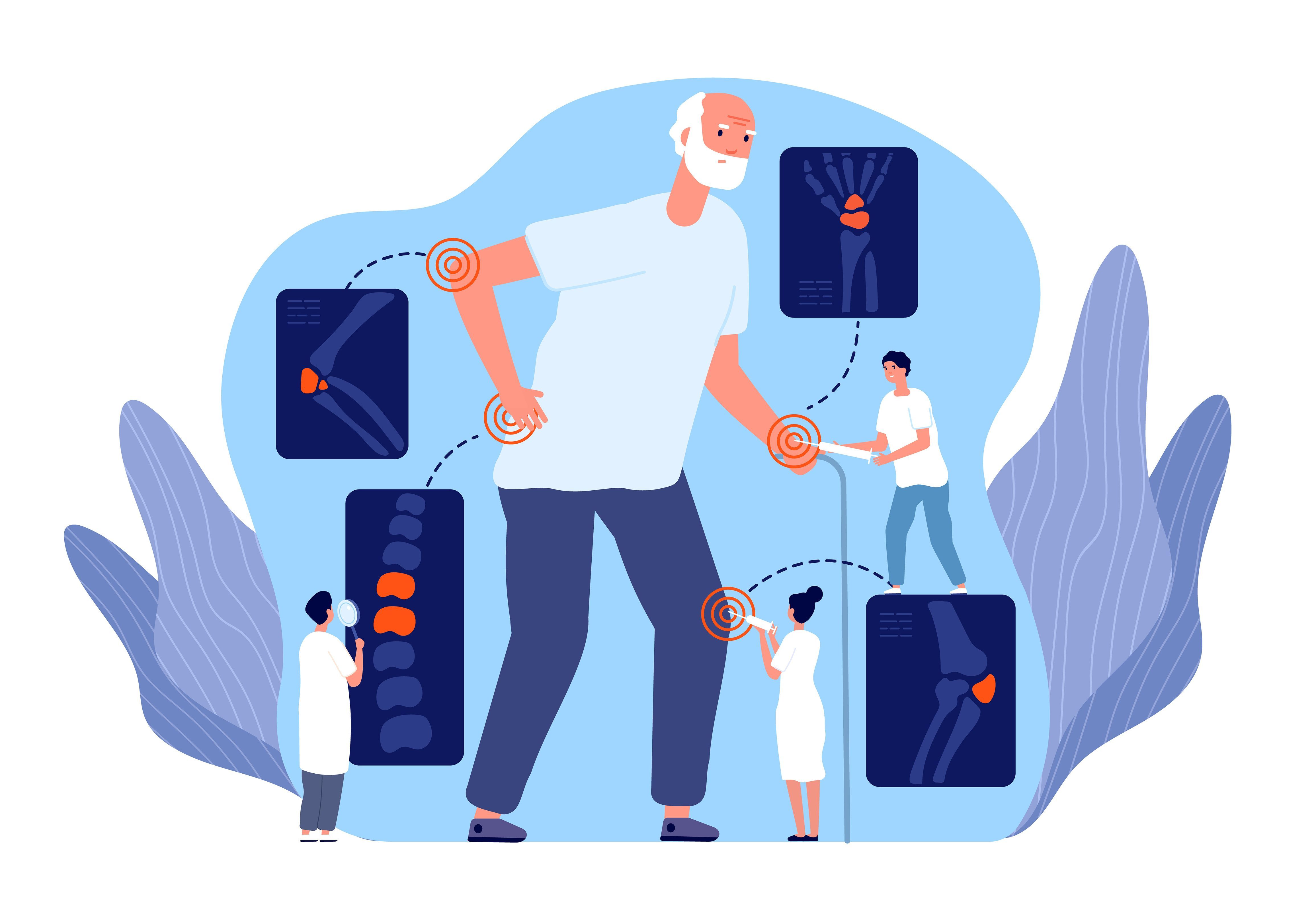
First, the researchers conducted a literature review on quality of care in rheumatoid arthritis that included relevant publications and guidelines from April 2005 to April 2021. A total of 114 academic and clinical publications were included in the review.
The review identified several challenges, including delays in patients seeking medical advice for undiagnosed rheumatology conditions, delayed referrals from primary care to rheumatologists, delays in diagnosis, delays in treatment initiation, poor adherence to therapy, a lack of monitoring by a rheumatologist, and unsatisfactory patient-reported outcomes.
Following the literature review, in-person visits were conducted with more than 50 specialists and health care professionals at 9 rheumatology centers in the United States and Canada to identify challenges and good practice interventions in rheumatology care.
During the in-person visits, researchers identified 8 interventions that helped alleviate challenges across the patient pathway, from awareness and prevention through referral, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up.
The interventions identified as high priority were:
- Using technology and data, such as developing digital resources to gather information or facilitate care coordination
- Streamlining rheumatologist care and treatment to minimize delays, which currently average 2 months from diagnosis to treatment initiation
- Promoting comorbidity assessments and support for patients, as rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased comorbidity rates.
These high-priority interventions were considered high priority due to their perceived impact on care implementation challenges, as well as the ease at which they could be implemented.
Other helpful interventions included:
- Initiatives to reduce funding barriers and give patients access to optimal medications
- Providing proactive psychosocial care to patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Collaborating efficiently across a multidisciplinary team to improve patient outcomes
- Providing an adequate support network to improve patients’ self-management
- Offering opportunities for health care provider education
“Although challenges in rheumatoid arthritis care and associated comorbidities are widely recognized, the results of the interviews attest to the findings of the literature review,” the authors wrote. “This study reports several challenges experienced by the centers across the patient pathway. To enhance patient care, it is recommended that centers establish and focus on the interventions that are most applicable to their patient pathway, population, and challenges.”
The authors acknowledged several limitations, such as the inclusion of only 9 centers, which limits the representation of different care models across North America. Still, the study developed good examples of rheumatology care that may also be implemented at other centers to improve care quality. While these findings are relevant, they still require validation.
“Further work is needed to explore the effect of implementing these interventions and whether they will improve quality practices in centers with [quality of care] gaps in rheumatoid arthritis,” the authors concluded. “Other centers may be able to apply these interventions by investing in enablers to improve rheumatoid arthritis care, such as conducting educational initiatives, building a technology platform, and improving collaboration with specialists in the community.”
References
1. Curtis JR, Bykerk VP, Crow MK, et al. Identification of gaps in quality of care and good practice Interventions in rheumatoid arthritis: insights from a literature review and qualitative study of nine centers in North America. ACR Open Rheumatol. Published online June 27, 2024. doi:10.1002/acr2.11695
2. Rheumatoid arthritis. World Health Organization. June 28, 2023. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/rheumatoid-arthritis
