- Center on Health Equity & Access
- Clinical
- Health Care Cost
- Health Care Delivery
- Insurance
- Policy
- Technology
- Value-Based Care
Antimicrobial Peptides Show Promise in Management of Atopic Dermatitis
Natural and synthetic antimicrobial peptides can penetrate deeper skin layers.
This article was originally published by Dermatology Times®. It has been lightly edited.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a class of peptides that are already present in the human body, and they have emerged as a natural alternative to traditional treatments of atopic dermatitis.
In a study published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences, Machado et al examined the current research on the use of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) to manage atopic dermatitis (AD), describing the sources, benefits, and limitations of AMPs. With their potential to manage the skin microbiome, fight infections, and modulate the immune response, AMPs offer a promising option for treating AD.
AD is a result of genetic changes that create an immune response and disrupt the skin barrier, with the most common mutations being associated with filaggrin (FLG) production and tight junctions mutations and alterations. Other structural proteins that are downregulated in AD include desmogleins, desmocolins, involucrin, and keratins.
The FLG disruption interferes with the production of moisturizing factors in the skin’s stratum granulosum, disrupts lamellar body section, and halts the metabolic pathway partway through causing an absence of acidic metabolites. This causes an increase in the stratum corneum (SC) pH and enables higher proteolytic enzyme activity and a higher growth of Staphylococcus aureus.
The pathophysiology of AD involves considerations of the environmental area, the skin microbiome, the epidermal barrier, and the immune or inflammatory response. Naturally produced AMPs have an important role in maintaining a healthy skin microbiome “through modulation of the microbiota composition, proliferation and death, and, thus, also play a role in the metabolites produced by them.” These peptides display antibacterial activity and exert immunomodulatory effects.
atopic dermatitis | Image credit: arhat - stock.adobe.com
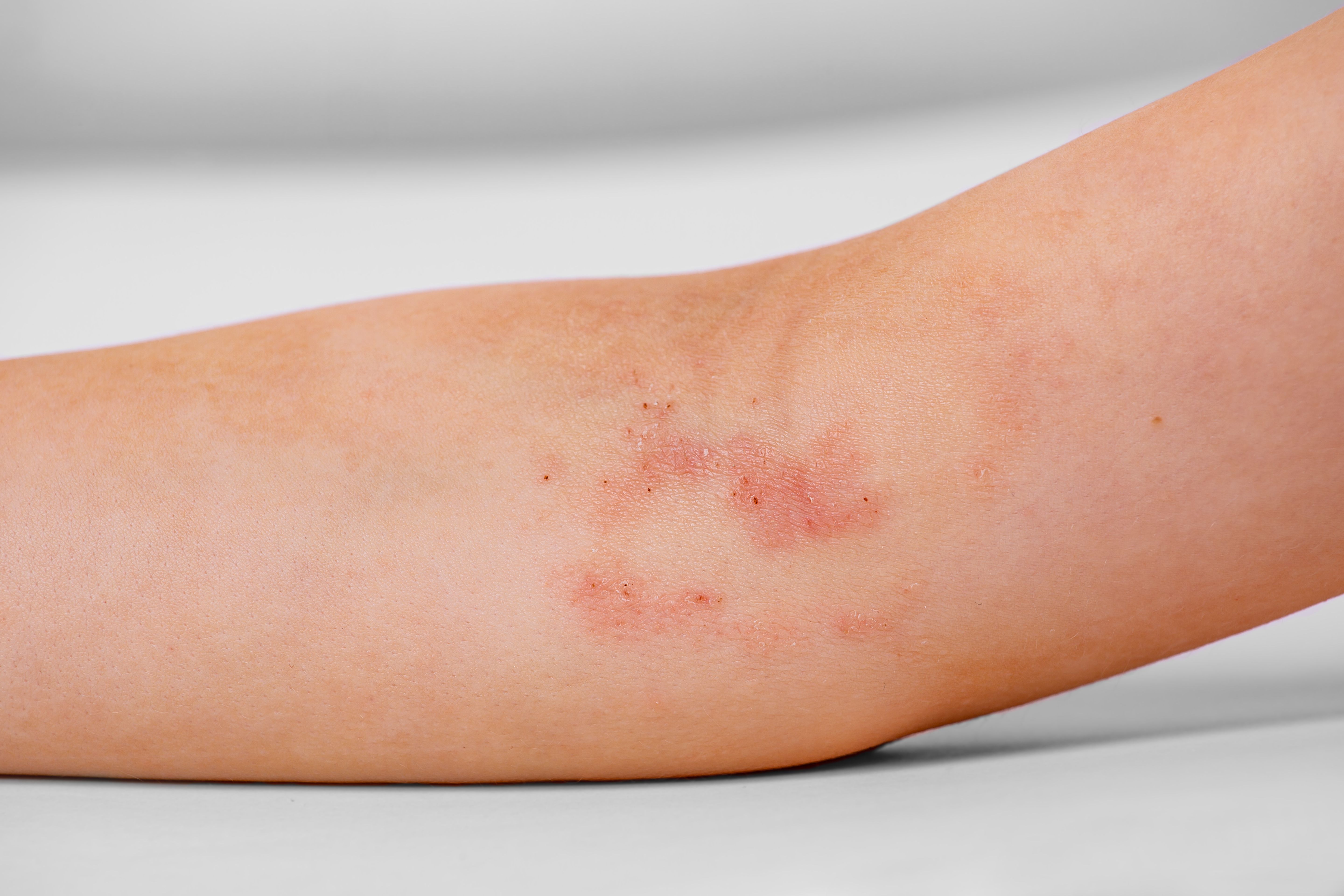
When AMP production is disrupted, patients with AD are more likely to experience skin infections from fungi, bacteria, and viruses. In patients with AD some AMPs, such as dermcidin and β-defensins, are underexpressed. Other AMPs, such as Rnase7, are overexpressed.
Recent research has focused on AMPs as an alternative to antimicrobials or as a pharmaceutical agent that can exert immunomodulatory activity. Natural and synthetic sources have been studied. Advantages of using AMPs include their ability to penetrate deeper skin layers, and “the fact that AMP-based treatment provides opportunities for interventions that closely resemble natural pathways and represent more of a replacement therapy than conventional treatment.”
Although some disadvantages to using AMPs have been reported, such as their rapid degradation by esterases or aminopeptidases, and their diminished stability in vivo, strategies to overcome these include penetration enhancers, encapsulation, and chemical modification to increase AMP permeability.
“[W]hile AMPs have already shown themselves to be natural and viable alternatives to conventional AD treatment regimens, and pharmacological solutions are already being explored and validated, there is still a way to go to enable AMPs to become cost-effective mainstream solutions for AD treatment,” Machado et al concluded.
Reference
Machado M, Silva S, Costa EM. Are antimicrobial peptides a 21st-century solution for atopic dermatitis? Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13460. doi:10.3390/ijms241713460
